Autumn is the second peak breeding season for rodents in a year, as outdoor temperatures gradually decrease and food shortages begin in the external environment. Rodents will migrate to residential areas, courtyards, basements, underground garages, pipeline wells, and other places, leading to a significant increase in indoor rodent density. Therefore, autumn is also the best season for rodent prevention and control. Improving rodent control measures at this time can effectively reduce rodent infestation in indoor living environments of residential areas.
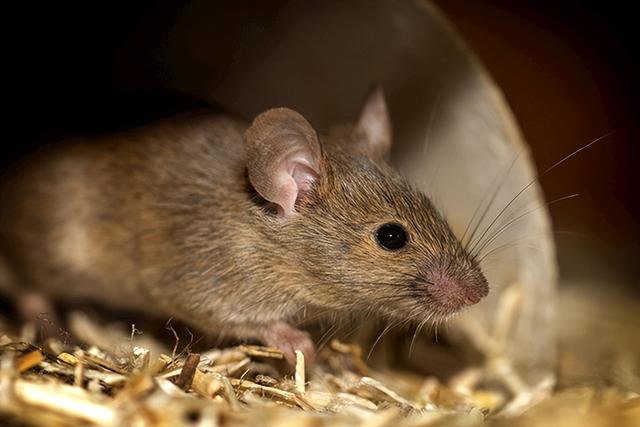

Common rodents in urban autumn include the house mouse, brown rat, yellow breasted rat, and a small number of black striped mice. According to the seasonal migration characteristics of rodents, rodent control should be carried out during the cool weather in late autumn, from winter to spring sowing or the early stage of awakening insects; And completed before the high incidence period of rodent diseases.
1、 Rodent density monitoring
Rodents have strong adaptability. Before autumn rodent control, the building type, garbage management, hygiene conditions, cleanliness of the environment, underground pipeline network, existing rodent prevention facilities, and rodent control facilities in the rodent control area should be inspected. Then, monitoring methods such as rodent trapping and visual inspection should be used to conduct a density survey before rodent control, in order to fully understand the degree of rodent damage, regional distribution, population structure, palatability, etc.
2、 Rodent control methods
1. Promotion
Street towns, communities, and village organizations should strengthen the promotion of rodent control in autumn and winter, mobilize residents, and encourage everyone to participate and interact.
2. Environmental prevention and control
Eliminate the breeding grounds of disease vectors such as weeds, debris, and construction waste in residential areas, especially in urban-rural fringe areas and around suburban residential buildings, to reduce the habitat of rodents.
Clean up household waste, cover the garbage bin, seal the garbage room, and reduce the source of rodent food. Fill the mouse hole and seal it with glass shards or brick debris mixed with cement.
3. Set up defense system
Improve rodent prevention facilities in areas such as doors, windows, air vents, underground pipelines, sewers, pipe openings, and wall openings to reduce the active invasion routes of rodents. Check the luggage, packaging materials, etc. inside the room to reduce the probability of passive carrying and intrusion.
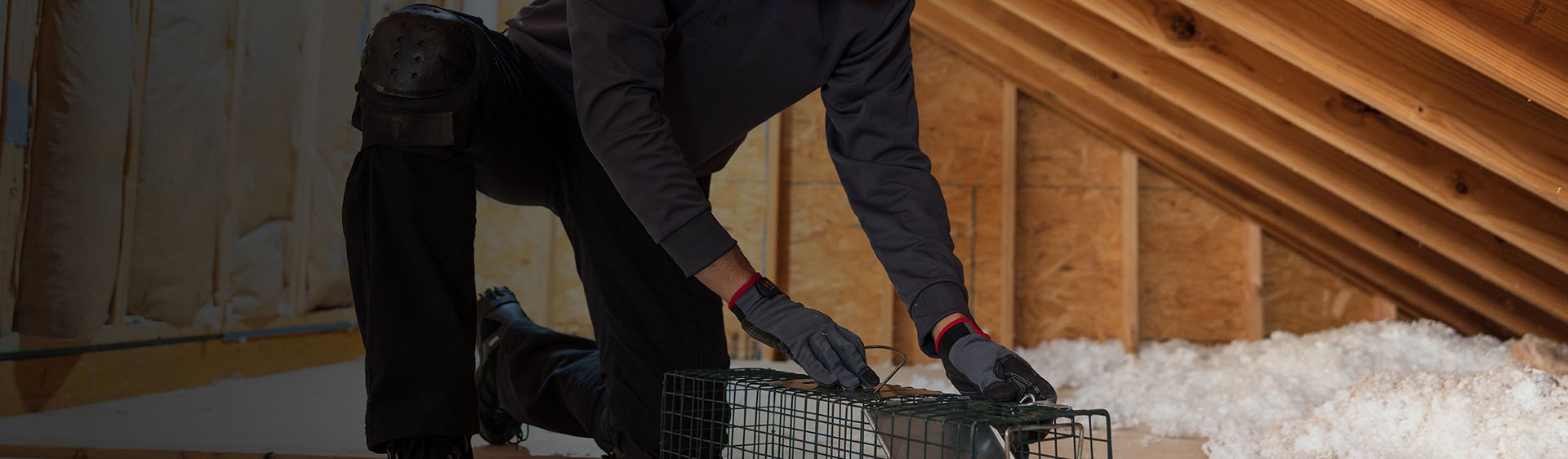
4. Physical control
Physical devices such as sticky boards, traps, and traps can be used to prevent rodent infestations. Long term deployment of physical instruments can be used to track and monitor rodents in specific local environments. Due to the adaptation of rodents to new organisms, newly placed or long-term deployed equipment has a lower capture rate for rodents.
5. Chemical control
The difference between various anticoagulant rodenticides currently lies in their varying levels of toxicity. Anticoagulant rodenticides can be divided into two categories, namely first generation and second generation products. The second-generation anticoagulant rodenticide has strong acute toxicity and can kill rodents that have developed resistance to the first generation anticoagulant rodenticide bait.
Rodent baits, self prepared rodent poison baits, and baits should be selected based on the rodent species or their palatability. Generally, local common foods are chosen as baits.
There are saturation feeding methods and targeted feeding for the release of rodenticides. Attention should be paid to checking the replenishment of rodenticides until they are no longer consumed.
6. Precautions
After dispensing rat poison, hands should be washed, and safety notices should be posted at the dispensing location. Attention should be paid to concealed dispensing or setting up poisonous rat rooms to prevent pets or children from ingesting it, and emergency response procedures should be equipped.
Rat carcasses should be collected and burned in a standardized manner or buried deep. If buried deep, it should be in a place that is not easily disturbed, at least 50cm deep. The backfill soil should be compacted tightly.